Introduction
The recent trends in global freedom have raised concerns about the future of democracy. The Freedom Report records that the global freedom index has constantly declined in the past fifteen years. For the most part, the democratic space is filled with autocratic leadership. In the past few years, the world has been characterized by increased violent conflicts, civil unrest, and the COVID-19 pandemic, further stifling the democratic space. Additionally, the scores in civil liberties and political rights have been falling as more than a few besieged democracies and authoritarian states embrace less democratic ways of power. In light of the ongoing trend, this paper seeks to discuss the forces pushing a democratic society into authoritarian rule with examples of practices in specific countries. The discussion also seeks to establish whether the slide can be averted or reversed. With the United States being the top democracy globally, it is vital to evaluate whether it can as well slide into authoritarian influence.
Examples of Democratic Sliding and Methods Used to Defeat Democracy
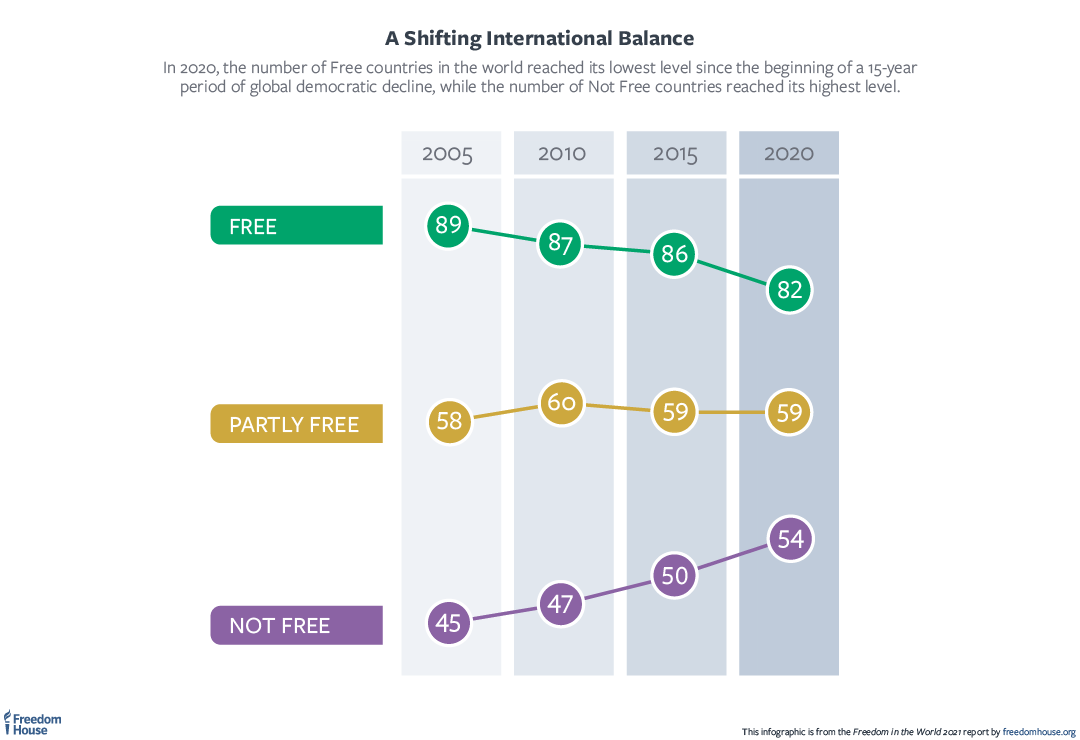
There are many ways countries slide into dictatorial governance, as the examples below indicate. The Freedom Report indicates that in 2006 only three countries in the world reported democratic sliding. The 2008-09 global financial crisis (GFC) allowed countries to exercise more authority and have strict power control. In line with the increasing stifling of democracy, by 2020, the number of countries with a reduced democratic space had gone up to forty-five. The report reveals that in 2020 the count of free countries across the world was at the lowest point over the 15-year period that has been characterized by democratic sliding. On the other hand, the number of not free countries was the highest. 2020 presented led to a further decline in democracy with the emergence of the COVID-19 pandemic.
One example that has shown democratic sliding is India, particularly in the current leadership of Narendra Modi. A relentless crackdown on criticizers has characterized Modi’s administration. The government also continues to curb the freedom and influence of human rights organizations, imposing strict sanctions on their funding and activities. Meanwhile, its ideology of Hindutva has sparked communal tensions. During the COVID-19 pandemic, India imposed tougher restrictions, including an inept lockdown that led to the careless and treacherous dislodgment of millions of internal migrant workforces. People highly expected that Modi would support democratic practices and a counterbalance to the totalitarian tenets in neighboring China and Russia (Waldner and Lust 110). On the contrary, he has been at the forefront of entrenching India’s authoritarian rule.
China has been the epitome of authoritarian rule globally for many years. China is the world’s most populated country under autocracy, and freedom is suppressed. The recent COVID-19 outbreak from the country’s Wuhan province shows how the country is led through censorship, negative campaigns, and widespread misinformation. The country’s leadership withheld crucial information and campaigned for a cover-up of the initial outbreak of the disease. As a result, the whole world came to be cruelly troubled due to China’s failure to request a swift overall reaction to the disease in its early days (Epshtein). The country also has featured predominantly in snooping in the local political dialogue of foreign democracies.
Furthermore, China exercises authoritarianism through the multinational extension of human rights manipulations common in mainland China. For instance, the country has been at the forefront in destroying the freedoms and legal sovereignty of Hong Kong. Besides, China has been able to gain influence in multilateral establishments such as the United Nation’s Human Rights Council (UNHRC). After the United States stepped back in 2018, China has pushed a vision labeled as non-interference that facilitates democratic sliding through the abuse of egalitarian doctrines and human rights ideals (Epshtein). The policy promotes the formation of autocratic alliances at the expense of punishing such tendencies.
Another country that has manifest democratic sliding is Belarus. The country has been in the spotlight for electoral malpractices, which saw the re-election of Alyaksandr Lukashenka. He has held the position of president in the country since 1994. The electoral body reported that he won the 2020 presidential election with over 80 percent of the votes cast, which marked his sixth term in office (Lindberg). Afterward, the outcome sparked large objections and demonstrations across different cities. The president exercised authoritarian influence by using the police and other means to attack the protesters, causing mass arrests and cruelty brutally.
Even as the majority of the nations are headed for poor democratic rule, a few examples stand out for their impressive effort in upholding and progressing democracy. The Freedom Report revealed that over 60 percent of democracies remained unchanged. They continued to talk about and practice political and civil democracy while a few showed improvement in supporting egalitarian principles, such as Malawi. The country held its national elections in mid-2019, but the outcome was contested in court through a landmark ruling that necessitated fresh elections. In addition, as leaders in other countries took advantage of the COVID-19 pandemic to squeeze the democratic space, the leaders in the Taiwan response fundamentally respected civil freedoms. It also benefited from the experience with SARS to respond effectively, emerging triumphant in its fight against the virus. The country also held free and fair national elections that saw the incumbent President Tsai Ing-wen re-elected into office.
Ways to Prevent and Reverse Democratic Sliding
The growing trend of democratic sliding can be prevented and also reversed. This strategy includes holding free and fair elections devoid of voter coercion, excessively clumsy registration rules, or exclusion. Nations also establish strong checks and balances that guarantee the autonomy of agencies and regulators the provide oversight and serve as a commanding check on any regime’s authority. Strong civil rights, individual freedoms, and equality before the law can ensure people raise against democratic sliding. The military should serve the citizenry and not the selfish interest of the leaders (Lindberg). Press freedom will help ensure correct information is communicated to the masses on the nation’s true state. The nations should embrace, support and empower vibrant civil societies that help to check the democracy trends.
Case of the United States
The United States, which is the biggest economy globally, is regarded as the home for democracy. However, this title has been shaken in the recent past, particularly under the administration of Donald Trump. In the days leading to the inauguration of the current U.S. President, Joe Biden, Donald Trump had refused to accept the election outcome and threatened to hold onto power. After the 2020 democrat victory, the majority of the republicans supported Donald Trump’s card of undermining accountability for wrongdoing (Aridi). He went ahead to fire some of the people who supported democracy, including the inspectors general in charge of digging out fiscal and other transgressions in government. Overall the party supporters intensified made-up accusations of voting fraud and fed the Americans with uncertainty.
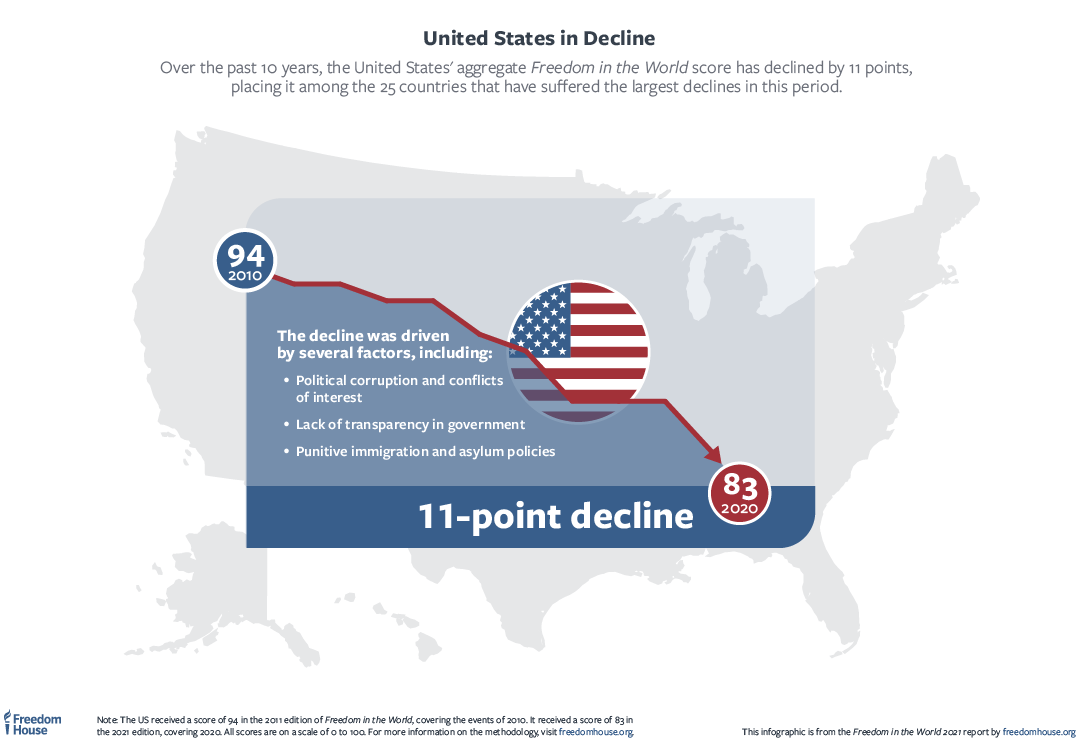
The events leading to the end of the Trump administration in the U.S. not only threw the country into an even bigger crisis but also exposed the country’s democratic weaknesses. Even though the nation could withstand the storm and usher in a new president, the country has to work forcefully to build up its institutional safety net. Still, much needs to be accomplished to protect the country’s respected democracy and salvage its global standing; if not, it risks descending into autocratic rule (Aridi). Additional measures required to prevent democratic sliding include re-establishing the national civic rule and supporting a democracy’s core philosophies.
Conclusion
In general, the world has reported declining democratic tendencies as leaders become more autocratic in their rule. Decreasing democracy is manifest through crackdown on media, false information, uprooting civil liberties, massive arrests, and disrespect for institutions, among other factors. Leading examples of nations with reducing democratic space include India, Belarus, and recently the United States. Malawi and Taiwan stand out as a few nations showing respect for democracy. Democratic sliding can be prevented and reversed if there are checks and balances, strong institutions and civil society movements, proper use of the military, and equality before the law, among other elements.
Works Cited
Aridi, Rasha. “How Democracies Are Now ‘Backsliding’ in Countries from Russia to the United States.” Science, 2020. Crossref.
Freedom House. “Democracy under Siege.” Freedom House, 2021. Web.
Lindberg, Staffan. “The Nature of Democratic Backsliding in Europe.” Carnegie Europe, 2018, Web.
Epshtein. “How Do Democracies Turn Into Dictatorships?” Renew Democracy Initiative, 2020, Web.
Waldner, David, and Ellen Lust. “Unwelcome Change: Coming to Terms with Democratic Backsliding.” Annual Review of Political Science, vol. 21, no. 1, 2018, pp. 93–113. Crossref.
