Introduction
Trade is an important component in the relationship between two countries. It is through trade that goods which are manufactured at one place find their way to places that they are not manufactured. Trade is also responsible for the movement of people from one area to another either on business duties or as tourists. This suggests that the main reason for trade is to take goods to places where they are needed. The global economy is actually driven by trade (Straight times 2011).
Countries in the world have formed trade blocks in order to establish strong partnerships on the grounds of trade that will enhance fairness between the two countries. Similarly, regional blocks have established a form of trade which ensures that goods are taken to particular markets in exchange of an equal reciprocation. A good example is the European and Asian trade partnerships. This paper discusses trade within this regional block (Bloomberg 2011).
Trade between Asia and Europe
The world has recently rebounded from a period of global downturn just. One of the regions that have led to the global economic recovery is Asia. This is because Asia had a quick recovery of its exports. Europe has been the major consumer of Asian products since time immemorial. The trade between Asia and Europe has continued to increase sharply even after the global downturn. It is important to note that after the period of global downturn that affected European countries, the recovery has rejuvenated the demand in the European countries for the Asian products. It is also worth noting that intra –Asian trade is a close competitor to the European market.
Although the recovery has seen a growth in the global economy, it is still worrying because the current developments in trade are not as good as they were in the recent past. One of the things that drive this rebound is the rise in demand. This has had an effect in shipping in that the business has become more lucrative. The rate increase caused by the increase in demand is also having a positive impact to the shipping industry since shippers are currently profiting from the rate increase (World Bank 2011).
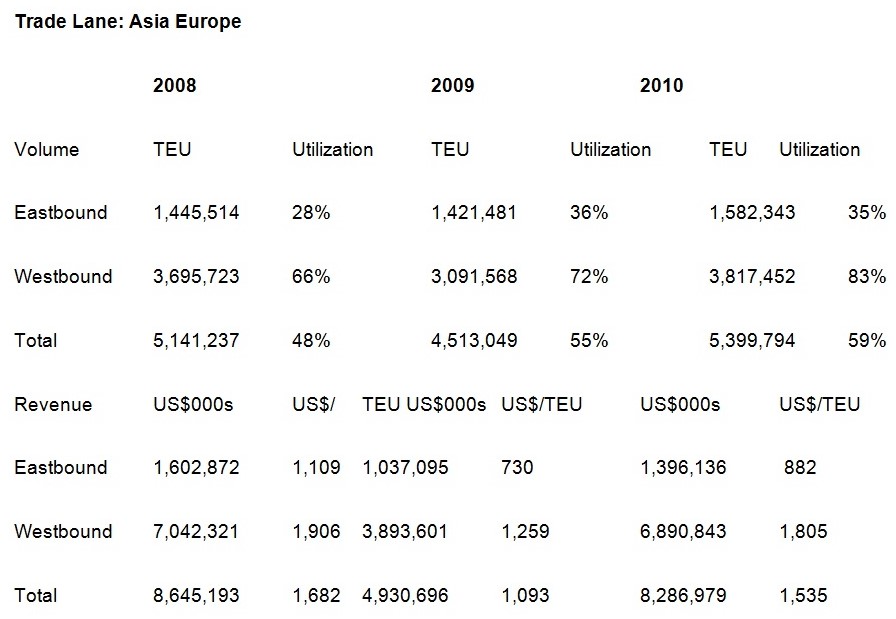
Trade between Asia and Europe involves goods such as agricultural products and commercial services. It is also important to note that the labor force also plays a vital role in trade between countries. A specific case study concerns the trade of commodity polymers between these two regions. Much as the global polyolefin trade volume increased in the year 2010, much of the global increased was as a result of the increase in Asia –European regional trade. During this period, there was also a pronounced shift in trade flows especially in the Asia -European trade region block (trade intelligence 2010). Thus, imports to china that had surged in the previous years rebounded in the year 2010. This had an effect on the global market. The effect caused slowdown of Chinese imports whereas there were significant gains in other Asian markets. Thus, the large volumes of imports in China in the year 2009, declined in the year 2010. There was also a resurgent in demand in Europe in the year 2010. This was because of higher intraregional trade and imports. Also, the increased global trade volume was a major factor for the decline in demands (Trade Arabia 2011).
Shipping lines that support the trade
There are a number of shipping lines that support the trade. The A.P. Moller-Maersk Group is a prominent player in this market. The company has recorded a ten per cent increase in revenue in the first quarter of the year 2011. This is direct evidence that the trade between the two regions is in the recovery path. Thus, higher container freight rates and increase in demand that has increase container volume are the major factors that have contributed to this success. The company is also contemplating increasing the rates further in order to cushion it from the downward spiraling of the trade. This decision was made by the Hanjin Company in mid May 2011 (business link 2011).
There is an overall slowdown in exports compared to the previous years before the economic turmoil rocked the world. The slowdown is also caused by the rise in U.S inventories and the waning growth in the European countries. These two factors are the main variables that are responsible for curbing the volume of shipments between these two regions. Many transport companies plying this trade route cite a number of reasons for the decline in trade and decrease in volumes of goods in transit. The Korean Airline cites the rising stockpiles of liquid-crystal display television to be among the major reasons that will cause the fall in demand later on in the year (Ifw 2011). Also, the Tennessee-based FedEx Corp. has recorded less than projected profits. This is because growth slowed in the rate of international deliveries whereas the cost of the deliveries rose. Although this issue is more serious than it seems, container shipping lines may still be able to stand the test and escape the consequences of this slowdown. One of the ways these companies are trying to do is by increasing the rates of deliveries (maritime logistics 2011).
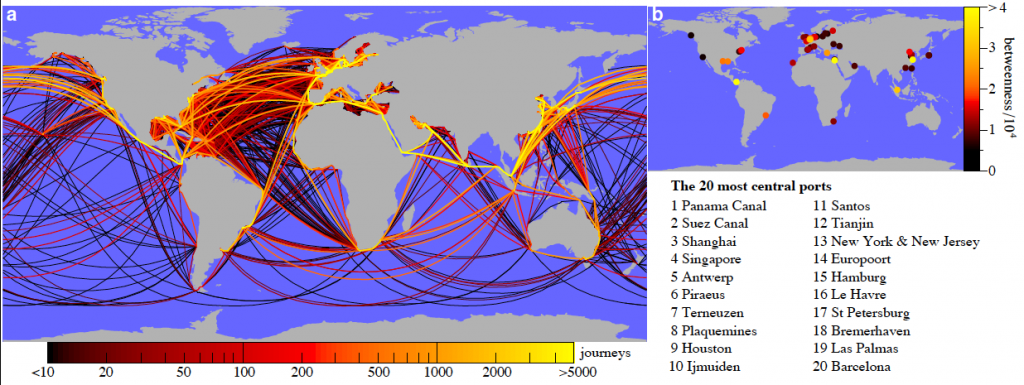
The main business routes from the UK moves towards Japan and china. This route passes through the Mediterranean Sea and through the Suez Canal. It also passes through the Malacca straights. There are also other established routes that serve Europe and the Middle East, Europe and India, and Europe and Australia (United Nations Publications 2010). These routes are mainly present where the trade volume is large and the demand is plenty. This is why there is a direct connection between the wealthy nations. The north Atlantic trade route is the busiest trade route (international Trader Publications 2011).
Apart from shipping lines that operate in the route, there are also airlines that carry cargo in the regional trade. The airline industry is mainly responsible for carrying passengers and cargo. This has increased trade within this regional block. Some of these airlines include the Scandinavian airline, Air France and Finnair.
For goods to be transported from Hong Kong to Malta there is a specific amount of time needed. Lead time is the time it takes the customer to order for goods and to receive the deliveries. The lead time to import in Hong Kong can be 5 days. This time is synonymous with that of Singapore. The lead time for UK can go up to six months or even more, while that of Le Harve can last between 2 to 4 weeks.
Conclusion
Trade is an important component in the relationship between two countries. It is through trade that goods which are manufactured at one place find their way to places that they are not manufactured. The world has recently rebounded from a period of global downturn just recently. One of the regions that have led to the global economic recovery is Asia. Trade between Asia and Europe involves goods such as agricultural products and commercial services. It is also important to note that the labor force also plays a vital role in trade between countries. The main business routes from the UK moves towards Japan and china. This route passes through the Mediterranean Sea and through the Suez Canal. Apart from shipping lines that operate in the route, there are also airlines that carry passengers and cargo in the regional trade.
Reference List
Bloomberg. (2011). Asia Exports Cooling Damps Outlook for Commodity Shippers: Freight Markets. Web.
Business link. (2011). Moving Goods by Sea. Web.
Box Trade Intelligence (2010). Container Shipping Business Performance-Q3 2010. Web.
Ifw (2011). Shipping Lines Succeed In Pushing Up Container Rates Out Of Asia To The US. Web.
International Trader Publications. (2011). World Trade Annual Reviews. Web.
Maritime Logistics. (2011). Maersk Goes For Rate Increase on Asia-Europe. Web.
Straight Times. (2011). Who is Buying Asia’s Exports? Web.
Trade Arabia. (2011). European Airlines Say Traffic Up, Asian Routes, Help. Web.
United Nations Publications. (2010). Trade Development Report. United Nations Publications. Washington, DC.
World Bank (2011). The Trade and Transport Integration Project Corridor Newsletter – (2010). Web.
