Abstract
Military technology has evolved significantly over the past century, with a notable shift toward the use of technologies allowing for greater precision and a much more devastating effect. However, the role of leadership in advancing technological progress in the military I not to be underrated; overall, the key military goals must define the future progress and the application of technological advances. For this reason, the increased focus on the enhancement of cybersecurity along with the rise in the use of robotics and the emphasis on building defense technology should be deemed as priorities.
Introduction
Over the past century, the military has undergone a transformation that can be described as quite impressive given the condensed time frame and the numerous goals that needed to be met. Specifically, targeting a broader range of objectives, the U.S. Army has been expanding the scope and extent of its opportunities, which, in turn, has extended to improving the technological performance within the military. The transformation has been truly massive, with significant changes not only in the use of technology but also in the leadership and overall goals. The importance of introducing cohesion into the performance of the U.S. military should be deemed as a particularly important issue to consider. While the incorporation of innovative technology and weapons is an admittedly useful change, it should only be regarded as a means to achieving the ultimate goals, namely, the enhancement of security and the protection of citizens. For this reason, apart from the promotion of the use of digital tools and frameworks in the U.S. Army context, a shift in the leadership approach and the overall perspective is required to achieve the set goals. Although the underlying intention of protecting citizens and reinforcing the political power of the state has remained the same from the 1812 War to the Desert Storm, the propensity toward shifting to the digital context and the focus on protecting the state from economic damage and the related cybersecurity threats as opposed to direct military interventions should be seen as the main direction in which the U.S. military technological development should be geared.
Literature Review
1812 War
The change in the use of technology in the war of 1812 was a truly remarkable trend. Specifically, the 1812 war represented a transfer from the cold steel weaponry, such as swords and bayonets, to the application of firearms, particularly muskets, rifles, and cannons (Zielinski, 2018). Although the specified weapons had rather small power compared to the present-day firearms, they did reinforce the efficacy of the attack and defense strategies used during the 1812 war (Zielinski, 2018). Therefore, apart from significant shifts in the sociopolitical climate on an international level, The War of 1812 also indicated a massive and unprecedented transformation of the U.S. Army due to the acceptance and use of firearms.
Specifically, the integration of firearms implied the need to move away from the strategies implying close battles and, instead, develop plans for distanced fights. The described change in the battle tactic has implied the creation of opportunities for the fights taking place on a significantly larger scale and with a larger set of stakes in mind. Consequently, the event in question can be considered a massive issue that has shaped the target audience’s perception of cultural differences, in general, and the ways in which cultural differences are perceived in a cross-cultural conversation, in particular. Namely, since the British troops had to fight indigenous American people in the specified fight, the integration of firearms provided British colonists with a tremendous advantage over the indigenous tribes, which resorted to the application of traditional weapons, such as arrows (Gilje, 2017). Therefore, the described conflict illustrates the importance of transferring to the use of innovative technology. Assessing the effects of the described change on the global setting and the independent goals of specific countries, one will have to concede that the increase in the frequency and efficacy of the use of firearms and the related weaponry has had a massively important effect on the U.S. military.
Desert Storm
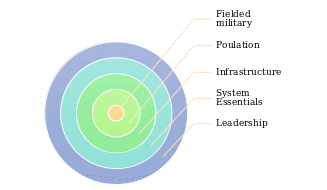
Being a part of a larger military campaign, namely, the Iraq War, the Desert Storm operation was supposed to assist the U.S. in advancing in the alien environment quickly and capturing the enemy’s positions swiftly. The operation implied the deployment of an innovative framework for managing military operations, namely, the Five Rings Model (see fig. 1 below). As shown in Figure 1, the framework in question suggested that the process of limiting Iraq’s power and addressing its invasion into Kuwait should occur by capturing the enemy’s forces in a physical paralysis. The specified effect was expected to be achieved by making a concerted effort of coordinating the fielded military, the population, the infrastructure of the operation, the system essentials, and the effective leadership approach. As a result, the U.S. Army gained a massive advantage of substantial flexibility in the context of the enemy’s setting (Zielinski, 2018). As a result, the U.S. military gained massive leverage in the war, causing the American troops to triumph eventually.
When considering the technological aspect of the specified operation, one should also mention the use of aerial bombardment as a method of forcing the regime to collapse and the enemy’s troops to yield. Thus, the technological aspect of the Desert Storm operation is surprisingly unremarkable since air bombardments have been in use as the tools for shaping the enemy’s response (Bralley & Fontenot, 2019). Consequently, the Desert storm operation has demonstrated the importance of a strategy over the use of specific weapons.
The described change in the perspective of the U.S. military could be seen as the starting point that marked the beginning of essential change. Indeed, after the Desert Storm operation, military endeavors have been defined by the selective use of leadership frameworks and the emphasis on a well-developed leadership approach. Specifically, the need to incorporate an integrated framework that could help coordinate leadership, the infrastructure, the system, the population, and the military, has become evident (Bralley & Fontenot, 2019). The significance of the specified integrated framework has been widely discussed in recent studies (Tagarev, 2018). For example, the paper by Tagarev (2018) proves the need to introduce a coordinated model that allows envisioning the army structure as a single entity. Therefore, the Desert Storm operation can be represented as the occurrence that allowed breaking new grounds in the development of innovative defense and attack mechanisms within the U.S. Army.
Finally, when assessing the specified military intervention, one must take note of the lack of cooperation and the presence of multiple arguments in the context of the U.S. Army. Specifically, the existing records point to the fact that there were significant disagreements and confrontations observed in the military environment of the U.S., particularly, among the members of American troops, during the Desert Storm operation (Bralley & Fontenot, 2019). As a result, the specified action did not yield the expected results, failing g to become the leverage for making the regime fall. Instead, the Desert Storm operation prepared the framework for the further destruction of the regime and the capture of Hussain, therefore, allowing the U.S. Army to free Kuwait. The specified discrepancy in the management of the operation proves the need for a comprehensive approach that allows encompassing the leadership-related issues, the assessment of the target environment, and the use of innovative tools for maintaining a strategic advantage.
Analysis and Lessons Learned
Both events discussed above provide quite profound and essential lessons for the U.S. military to learn. Specifically, the 1812 conflict. Namely, the war of 1812 proved the transformative role of technological innovations in the military, demonstrating the strategic and tactical changes in the approaches used by the troops when fighting the enemy. Namely, the integration of firearms into the fight signified the absence of the need for close fights and, instead, required redefining the approach toward the strategic placement of the troops within the battlefield (Sunik, 2018). Therefore, the 1812 experience was an undeniably crucial lesson to learn for British forces and a tragic outcome for Native American residents. With the introduction and active application of firearms, such as muskets and rifles, the colonists received a tremendous boost in their further endeavors at capturing northern American territories, while indigenous people had no other opportunity but to retreat.
In turn, the Desert Storm operation has shown that the use of innovative theories when planning a military attack is just as important as the integration of new firearms and the relevant devices. Specifically, the Five Rings Model, which was an innovative strategy for the U.S. military at the time, led to the complete physical paralysis of the enemy, causing the U.S. troops to triumph in the end (Sunik, 2018). Thus, the Desert Storm case showed the importance for the U.S. Army to evolve and incorporate new ideas and frameworks into its approaches toward defense and attack. Specifically, the necessity to recognize the role of new frameworks for managing military tasks has become evident with the implementation of the operation.
Particularly, the Desert Storm plan has proven the importance of transferring toward the framework that involved an integrated approach based on coordinating different aspects of the operation management framework., By viewing the subject matter as a single entity and planning the further steps based on the analysis of the outcomes for each specific aspect of the plan, the U.S. Army managed to achieve complete success. Specifically, the deployment of the Five Rings Model has proven the need to ensure that the five elements of the system, namely, the field military, the population, the infrastructure, the system essentials, and the leadership approach, are fully compatible and coordinated.
Future Challenges
The further incorporation of technology into the context of the military setting in order to maintain a strategic advantage while also ensuring that the extent of the army security remains high is bound to become an absolute necessity. Specifically, a shift toward the use of tools geared toward enforcing cybersecurity in the army can be predicted for the U.S. environment. The described change is justified by the increasing importance and threat of cyberattacks that the U.S. army has been witnessing over the past couple of decades (LaRocca et al., 2018). Specifically, due to the rise in the number of cyberattacks attempted at the U.S. Army and the possibility of a massive data loss that the described threat implies, the role in the enhancement of the U.S. military data security becomes all the more obvious.
For this reason, the integration of tools of detecting threats of cyberattacks and developing strategies for mitigating them can be considered some of the most likely changes to be observed in the future in regard to the management of cybersecurity issues in the international context for the U.S. Army. Additionally, the necessity to manage an increasingly large number of data that is defined by a uniquely large number of factors should be mentioned as one of the major trends in the transformation of the U.S. military setting. Specifically, studies illustrate the need to integrate Big Data into the evaluation of global threats to U.S. military data security and the enhancement of the safety of citizens’ private information. To restore some semblance of peace and composure in the target context, one might want to consider assessing the effects of the described conflict to occur in the U.S. political landscape (LaRocca et al., 2018). Namely, the losses that the U.S. Army is likely to incur as a result will not affect the state to the same extent with the cybersecurity tools incorporated into the target setting compared to the damages that are likely to occur once the issue of security breach occurs. Therefore, the development of a framework trustworthy enough to contain the threat and minimize exposure to cyberattacks while remaining easy to use for the U.S. Army members represents a major challenge. Additionally, teaching staff members and troops to utilize cybersecurity tools in a way that minimizes risks suggests additional challenges. Nevertheless, with the introduction of a proper leadership framework, the specified obstacle will be overcome successfully.
Furthermore, the integration of innovative technology into the military setting and its further use for military purposes may imply facing several complications. For instance, the inclusion of robotics into the target context should be seen as vital given the massive opportunities that the AI tools provide for maintaining security and ensuring that the threats associated with the possibility of an intrusion are successfully mitigated. However, the introduction of AI, VR, and related technologies into the military setting will suggest not only changing the infrastructure drastically but also training staff members to develop the skills needed to navigate the specified technology flawlessly. Given the urgency of most army-related tasks and the importance of a prompt response, the proper training is likely to require a tremendous amount of time and a massive effort that will demand substantial financial resources. Thus, the U.S. Army may not be ready for the specified extent of expenses.
To adders the specified issues, the U.S. army will need a change in the leadership framework. Particularly, the focus on promoting connectivity between leadership, key operations, the infrastructure, and the related processes will be needed. Additionally, staff members and officers will have to be instructed on the use of innovative technology so that it can be integrated into the context of the U.S. military setting and the associated decision-making accordingly.
Conclusion
While remaining vigilant to protect the state against the threat of a physical military intrusion is still relevant, the focus in the reinforcement of the military power and the transformation of the U.S. Army should be kept on fostering the introduction and active use of digital tools for enhancing cybersecurity. Due to the devastating impact that cyberattacks can produce, particularly the theft and misuse of government data, the U.S. may be exposed to a significantly broader range of threats if the technological aspects of its military defense are not reinforced accordingly than it would be if it had certain dents in its traditional military defense. Given the shift from the physical military space for confrontations to the realm of cyberspace, it will be vital to focus on incorporating innovative technological solutions into the present U.S. military context. Furthermore, the focus on the education of the troops, as well as officers, will have to be seen as an essential goal since it will allow improving the use of innovative tools and their integration into the key operations successfully. Namely, innovative devices and software for managing information and identifying critical threats to citizens’ well-being, as well as state security, in general, must be integrated into the U.S. military context. Moreover, the proposed change will allow reinforcing the connectivity between the essential processes within the U.S. army, causing a large improvement in strategic and tactical decision-making. Thus, the safety of citizens and the security of the state will be kept at properly high rates.
References
Bralley, N. H., & Fontenot, G. (2019). The 1st Infantry Division and the US Army Transformed: Road to Victory in Desert Storm, 1970–1991. Naval War College Review, 72(2), 19.
Gilje, P. A. (2017). Commerce and conquest in early American foreign relations, 1750–1850. Journal of the Early Republic, 37(4), 735-770.
LaRocca, M. A., Scogin, F. R., Hilgeman, M. M., Smith, A. J., & Chaplin, W. F. (2018). The impact of posttraumatic growth, transformational leadership, and self-efficacy on PTSD and depression symptom severity among combat Veterans. Military Psychology, 30(2), 162-173.
Sunik, A. (2018). Regional leadership in authoritarian contexts – Saudi Arabia’s new military interventionism as part of its leadership bid in the Middle East. Rising Powers Quarterly, 3(1), 65-85.
Tagarev, T. (2018). Hybrid warfare: Emerging research topics. Information & Security, 39(1), 289-300.
Zielinski, R. C. (2018). How do war financing strategies Lead to inequality? A brief history from the war of 1812 through the Post-9/11 wars. Studies, 16(1), 59-80.
