Introduction
A country’s economic stability or instability is determined by various factors in the economy, which guide the economic goal of a country. Various scholars and researchers have developed economic concepts used to explain both the macroeconomics and microeconomics of individual countries. The following discussion analyzes different economic terms and the effects of trade tariffs on the economy.
Intra-Industry Specialization
Intra-industry specialization is the industrial specialization in a specific market or line of production triggered by the scale of economics. Industries in a particular line of products in the same geographical area may decide to specialize in a single line of production to improve their return on investments. When the scale of economics is high, businesses, tend to specialize to take advantage of the available economic growth opportunities. Specialization in intra-industry increases the marginal opportunity cost for companies. If the government develops policies that favor trade specialization, industries in the country find it necessary to specialize in their line of production.
Inter-Industry Specialization
Inter-industry specialization is defined as the specialization of different manufacturing companies in various geographical locations but in different sectors. Mostly inter-industry specialization is influenced by intra-industry specialization where they seek to increase their returns by utilizing market opportunities presented by trade specialization. Countries with equal economic power and opportunities have a high level of inter-industry specialization. For instance, countries with a trade agreement on a particular product may trigger inter-industry specialization since; industries in both countries will use the trade agreement to increase their economies of scale.
Domestic Product Subsidy
A domestic production subsidy is the trade incentive provided by the government to encourage and improve domestic production. States may provide these trade incentives through tax reduction or cash payment for domestic production. Subsidies encourage investors to invest in a particular industry since the government has provided an economic incentive for them. For instance, the government may lower milk export tax to encourage farmers and other investors to increase their milk export. Mostly subsidies are issued in areas where the government feels that there are opportunities for growth, but the current trade policies do not favor particular investors such as youth or women.
Types of Trade Tariffs
Tariffs are trade taxes involving exports and imports of particular products and services. The government uses tariffs to raise revenue and control the trade of certain goods and services. There are several types of trade tariffs, which include: first, specific duty. This type of tax is levied based on the particular physical characteristics of a product. Physical characteristics include the weight and size of the product being imported or exported from a country. The second type of tariff is an ad valorem duty. This type of tax is imposed based on the value of the commodity being imported or exported. Ad valorem taxes are imposed on products whose real value cannot be determined based on their physical characteristics. The third type is compound or combined duty. This is a combination of both ad valorem and specific taxes on particular products. The fourth type is sliding scale taxes. This is the tariff where the tax amount is determined by the price of the commodity in the market. Sliding scale duties are not constant since the prices of goods may vary in the market. The fifth trade tariff is countervailing duties. Countervailing taxes are levied on imports, which the exporting state has issued subsidies on the products. The aim of this tariff is to reduce the effects of product subsidies issued by the exporting government. It is an addition to the ordinary levies imposed on the same product but with no subsidies.
The sixth type of trade tariff is the revenue tariff. This is the type of tax imposed on luxury goods being imported into the country. The aim of this type of tax is to provide the government with an extra source of income. The seventh type of tariff tax is anti-dumping duties. Dumping is the situation where exporters, export particular products at a cheap price to utilize a foreign market opportunity of the products. Dumping may cause local investors to make losses; therefore, governments tax such products to protect local industries. The final type of tariff is protective tariffs. This is the type of tax imposed on particular products to protect the local industries. The protective tax aims at discouraging importers from importing certain products. Trade tariffs may be levied based on an international agreement between countries.
Offshore Assembly Provision
The offshore assembly provision provides preferential tariffs on products produced abroad, but have been manufactured using United States components upon their reentry into the U.S. Market. These regulations have increased the demand for goods produced in other countries, but using U.S. raw materials.
Bonded Warehouse
A bonded warehouse is storage controlled by the customs authority where imported products are stored until the importer pays all the taxes imposed on the goods. There are tax provisions where the government asks importers to store their products in the warehouse for the sole purpose of re-exportation, and they will be exempted from import duties. This rule lowers the level of tax collected by customs authorities hence, reducing the government revenue.
Foreign Trade Zone
Foreign trade zone lowers the level of tax collected from a company since some products are exempted from customs duty. Businesses can befit from these provisions through duty elimination, drawback, deferral, and reduction. Foreign trade zone enables companies to export and import goods at a competitive price, hence improving their profit level.
Economic Model for Trade Tariffs Effects on the Economy
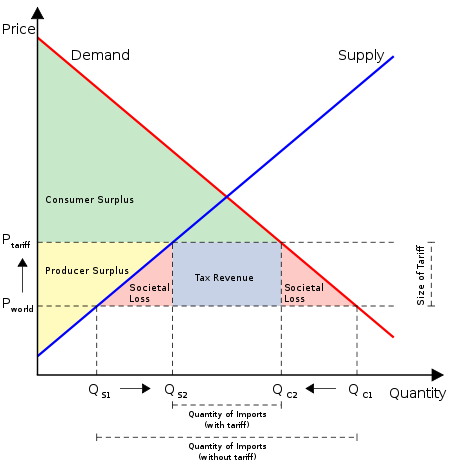
The above graph shows the effects of tariffs on a country’s economy. Before-tax, the prices of the products were in P world, however, after custom tax, the price of the product increased to P tariff. From the graph above, the increase in tariff reduces the level of consumer surplus due to the high cost of goods. Tariff increases the level of producer surplus and the revenue generated by the government from the duties imposed on products. High tariff reduces consumer surplus by a huge margin compared to the government and producers’ gains. Trade tariff affects both the demand and supply of a particular product. High tariffs make it expensive to export or import a particular product making the product expensive in the market. Consumer demand for expensive products reduces hence reducing the supply of the goods in the market.
Optimal Tariff
An optimal tariff is a government tax plan aimed at maximizing tax revenue to improve the welfare of a country. The primary function of this type of tax is to increase the state’s income from imports and exports. I believe optimal tariff is achievable, but only for countries with a high level of economic power. Small countries may not benefit from optimal tariff since it reduces the demand level of particular products. Increasing the tariff level directly affects both the demand and supply elasticity in the market. Currently, it is impossible to achieve optimal tariffs due to globalization, which has increased the level of competition forcing states to issue subsidies for local investors. In addition, most countries have joined trading blocs that have a trade agreement involving trade tariffs.
Tariff Effects on Exporters
Tariffs can be a burden to exporters due to the following reasons: First is double taxation. Double taxation occurs when a product is taxed by both the exporting and importing countries. This increases the cost of the product, which may reduce the demand for imported goods resulting in losses for exporters. Protective tariff prevents discourages exporters due to the high taxes aimed at protecting local investors. High tariffs affect the consumers’ discretionary income since they have to spend more on a product if they wish to purchase it. Taxes increase product prices, making it expensive for consumers to buy the product. They have to spend more cash if they want to buy imported products.
Difference between Tariffs and Quotas
States impose quotas and tariffs to control both imports and exports. Tariffs are the taxes imposed on imports and exposed while quotas are government restrictions on import and export quality. Tariffs and quotas affect the economy differently due to their distinct purpose. Quotas ensure that consumers get the best quality products and protect investors from counterfeit goods. Tariffs have both positive and adverse effects on the economy. On the positive side, tariff increases government revenue, which funds the budget. However, taxes, raise product prices, which may lead to inflation.
Domestic Product Protection Policies
Domestic production can be protected through several policies, which include: first increasing import tax of similar or subsidiary products produced locally. This will increase the prices of foreign products, which will reduce their demand level in the country. The second method that can be used to protect local products is through a government ban on the import of particular products manufactured locally. For instance, the government can restrict the importation of sugar to protect local sugar manufacturing companies.
International Trade and Labor Migration
International trade can be a substitute for labor migration since, industries and governments can import products, which they do not have individuals with the skills and techniques for manufacturing. Instead of outsourcing people with the skills required to manufacture certain products, industries may opt to import finished products. For instance, a company producing cars may decide to import engines if they do not have employees who have the skills required for the production of car engines. There are various factors that affect labor migration, which include: first, the ease of getting a work permit for international employees. If it is difficult for a foreign employee to acquire a work permit, then the labor migration rate may be affected. The second factor is security. It is difficult for individuals to migrate to countries experiencing security threats due to fear of their lives and properties.
Conclusion
In conclusion, trade tariffs are a primary source of revenue for many countries due to the growth of international trade. Countries protect their local investors by restricting the importation of particular products in the country by raising import duties. High tariff rates may affect demand and supply elasticity since it increases product prices. Quotas ensure that the products imported into the country meet certain quality standards to protect consumers and investors from a counterfeit or inferior products. Government subsidies ensure that local investors have a healthy business environment to develop their products.
