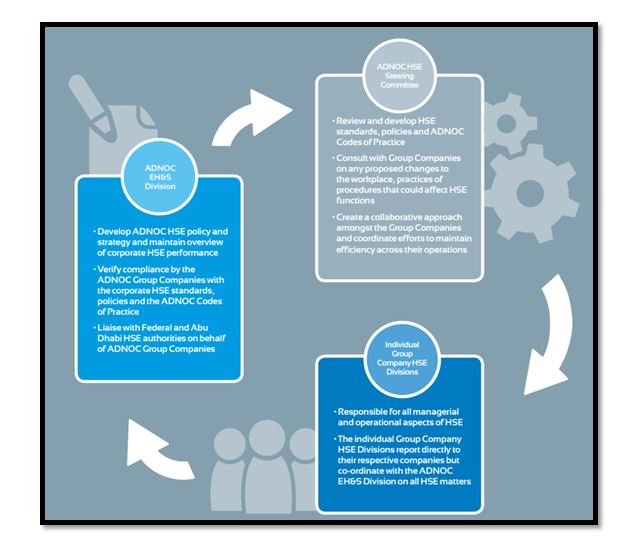
Introduction
On 17 April 2007, HH Sheik Mohammed bin Rashid Al Maktoum stated that the UAE Federal Government would be launching the first iteration of the Strategic Plan in 2008-2010. Accordingly, all ministries and federal institutions were entrusted with developing strategic and operational programmers and creating a new department, dubbed strategic planning and performance management, in their organizational structures. It was assigned to the new department to manage the creation of the entity’s strategy and operating plan in line with its management vision and the Prime Minister’s Office’s directions. This declaration marked a fundamental transformation in governance, from conventional government control to management with long-term strategic aims and goals. However, government agencies were not prepared for this qualitative transformation in this era. Thus, the prime minister’s office conducted several meetings, seminars, and workshops to bridge the gap and prepare federal authorities for the next stage and their responsibilities (El Khatib, Al Qurashi, Al Brieki, & Management, 2021).
Challenges faced by the Ministry
In addition to the modern concept of strategic planning and the lack of information, knowledge, and supporting tools for the management of public performance in 2007, some departmental heads, together with most of their staff, mainly elderly, expressed their silent objections or their lack of enthusiasm for the new concepts. However, the rigorous engagement of leadership in changing and supporting their dominance has helped many overcome and reduce this difficulty. There was a lack of government-wide operating structures and templates. Moreover, this encouraged the team to design their templates and business models in a more straightforward style that would satisfy the fundamental needs of implementation and would not strain users. The team utilized templates from Microsoft Excel to build operational plans for its initiatives and projects since most staff were acquainted with them (Alhammadi, Tham, & Azam, 2020).
The planning phase authorized 47 projects for 2008. The plans comprised around 3,000 actions and more than 300 strategic and operational indicators, which need regular monitoring and review. After six months, the performance evaluation showed that it did not achieve its objectives, and the team needed at least three times to raise their team size or leverage IT skills for the same reason. Furthermore, technology was designed to minimize the risk of mistakes by many users who participated in feeding and managing the plan, facilitating data updates, and easy document attachment. In addition, the shortage of time available to satisfy the criteria of the Office of the Prime Minister increased the number of difficulties and the risk percentage.
Sustainability of alternatives
The answer to these difficulties lies in the usage of IT. The use of IT offered increased accuracy, speed, and ease of follow-up without double the number of employees. Therefore, it was necessary to develop a technical solution that allows departmental managers and senior leadership in the Ministry to monitor the progress of plan preparation from time to time without the need for manually created reports. Using IT skills, the team had three possibilities to evaluate: 1. internationally prepared ERP solutions from companies such as IBM, SAP, JDE, and Oracle. This option is built on best practices, was dependable and available at a high level, and is continuously improved and supported after buying. However, this approach was expensive and offered several functionalities that the Ministry did not need and required extensive user training. 2. The purchase of one of the other prepared strategic planning solutions, for example, Cascade, Envision, Strategy, Corporate, and Cubes. This choice is less expensive than the preceding one. It had many unneeded capabilities or features, but it was insufficient in dependability and unclear in providing continual development and support after purchase. 3. Build an in-house application utilizing the SharePoint platform coding language ASP.net based on the department’s acquired knowledge and actual demands. The internal application might be cheaper, easier to manage, quicker to change, and more user-friendly. However, dependability difficulties may arise in the future (Al Darwish).
Proposed alternative
Index of Opimism is at 0.60 (60%)
MaxMax:
- International ready-made ERP solution = 1250000/0.60 = 2083333.33
- Ready-made strategy planning solution= 12750000/0.6 = 21250000
- Build in-house solution =21950000/0.6 = 36583333.33
- Decision = Build in-house solution because it has the maximum value (Marchau et al., 2019)
MaxMIn:
- International ready-made ERP solution = 1250000/0.40 = 3125000
- Ready-made strategy planning solution = 12750000/0.4 = 31875000
- Build in-house solution =21950000/0.4 = 54875000
- Decision = Build in-house solution since it has maximum of the minimum payoff (Marchau et al., 2019)
Realism:
- International ready-made ERP solution = 1250000/0.80 = 1562500
- Ready-made strategy planning solution = 12750000/0.8 = 15937500
- Build in-house solution =21950000/0.8 = 27437500
- Decision: Build in-house solution because it will maintain the status quo (Marchau et al., 2019)
Average:
- International ready-made ERP solution =1250000/0.60 + 1250000/0.40= 5208333.33
- Ready-made strategy planning solution = 12750000/0.6 + 12750000/0.4 = 53125000
- Build in-house solution =21950000/0.6 + 21950000/0.4 = 91458333.33
- Decision: Build in-house solution because it is maximum (Marchau et al., 2019)
Regret Table:
- Decision: Build in-house solution since it has the highest expected value
Optimizing ADNOC with effective decision making
The entire organizational culture of ADNOC helps them to achieve excellent outcomes. Internal human resources procedures must be more focused on building interactions with workers to be more ready to achieve excellent outcomes in their tasks. The company’s talent management strategies also allow managers to make their staff more competitive in their jobs, enabling them to attain excellence over the long term (Al-Hosani, 2011).
It features efficient recruiting and selection procedures that attract highly skilled workers that can exceed the management expectations. This method will thus allow the company to grow the value of its internal operations in the sector on a long-term basis.
The motivation theory of Maslow allows an organisation to grasp particular objectives in its operations. It, therefore, enables a leader to comprehend all workers’ demands and how they are likely to influence their capacity to provide effective outcomes (Alhammadi, Tham, & Azam, 2020).
More significantly, it helps workers find out what unique difficulties make them a company and what they can benefit from by being long-term faithful to their fundamental principles (Alhammadi, Tham, Azam, & Studies, 2020).

ADNOC is one of the world’s major oil and gas producers. It understands the benefit of integrating AI into its business processes to optimize operations, increase recuperation, and better decision-making. ADNOC leads the implementation of AI by improving the study of hydrocarbon resources in Abu Dhabi (Al-Hosani, 2011).
ADNOC has already succeeded in using AI to increase geological research. Although rock samples must continue to be scanned and booted manually, picture categorization is quicker and more automatic today. Since Watson can evaluate 527 photos per second, it takes minutes – not months – to examine all the samples obtained from a single reservoir.
The validity of the geological model is the basis for the predicted accuracy of a reservoir simulator – used to inform management choices on multi-billion dollar field development. Geology depends on visual microscopic rock depictions using an optical microscope in a lengthy work-intensive procedure, which has not altered since modern geology began in 1793.
In addition to increasing classification speed, ADNOC’s team already has numerous other significant benefits from the Watson-driven AI solution. For example, with the analytical time decreased considerably, ADNOC can examine many more rock samples, yielding more predictable data from many more wells. In turn, this leads to more precise and efficient subsurface models. In addition, Watson’s AI libraries provide ADNOC a means to maintain the decades of expertise of its petrography without the years of bringing fresh specialists up to speed. “The solution enables us to open the time for our geologists to concentrate on model production and to transfer our specialists’ expertise and expertise to the machine so that we may use their expertise when they move forward.”
ADNOC’s problems encounter certain obstacles in operations and management (Adgeco.com 2020). In this task, the firm examined tries to reinvent itself in order to rival multinational petroleum firms. This management task shows that the corporation monitors its partial privatization strategy and brings key partners for export markets and global operations. On the other hand, it illustrates that foreign operations and exports are relatively strict. The integrated 2030 approach also has several problems, notably for the COVID pandemic. As a result, the corporation plans to revamp its strategy, but all business strategies must be considered. All this, however, will create much uncertainty among workers at work (Alhammadi, Tham, Azam, et al., 2020).
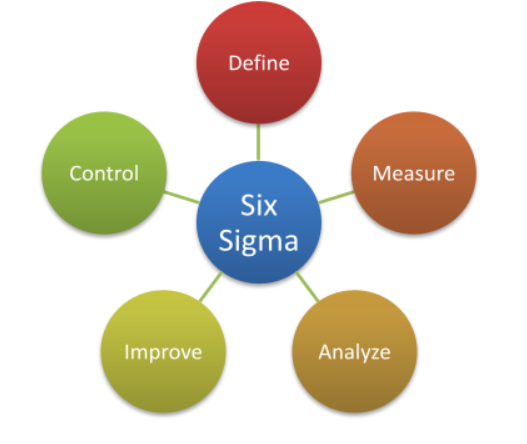
The issues stated by ADNOC in the operational management task may be overcome by Six Sigma’s philosophy of operational management. It helps improve operational quality and reduces mistakes and faults. As a result, the entire operating costs of the firm are lowered over time. ADNOC must follow five processes in the Six Sigma Theory in order to resolve difficulties. Firstly, the expectations of consumers should be determined worldwide. The measurement should then be carried out to determine the modifications necessary to achieve the objectives. In the operational management task framework, the underlying cause of the problem should be adequately recognized and analyzed, and changes should be made. There should be a control method to meet all the objectives of ADNOC. The staff should be taught to the highest level, and support infrastructure for success should be built. The task of operational management investigates the words of Hammer 2019, p. 175, that long-term objectives should not initially be envisaged. Instead, the organization has to focus on short-term objectives so that ADNOC can grow the worldwide market. The emphasis should only be on process improvement (Cheaitou, Larbi, & Al Housani, 2019).
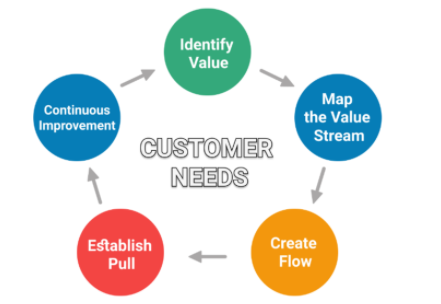
Lean manufacturing is another operational management idea that many businesses in today’s world adopt. The lean manufacturing process focuses on waste reduction and productivity improvement. As a result, the lead times and operating costs are decreased. This notion, exemplified in the management task of operations, serves to improve product quality. In order to manage worldwide growth, ADNOC should aim to adopt this principle in the manufacture of new goods and geographical growth. The organization’s administrators will have to think of methods to coordinate human activity to provide optimum society advantage. First of all, ADNOC will have to comprehend the consumers’ viewpoint. In this case, the following stage is to map the value stream, and the third step is to establish a flow by identifying all the obstacles. The fourth phase is a pull system that represents the start of some new job. The latter will concentrate on ongoing improvements. All of these ideas and ideas presented in the operational management task will contribute to ADNOC’s plan for 2030.
Conclusion
It intends to increase the thin rock image section data from the Abu Dhabi subsurface to a large extent. Many of our management and development choices are dependent on the characteristics and interpretations made by our petrography. As more information, we can utilize, our models, development plans, and final hydrocarbon regeneration will be better and more efficient. It is essential to our industry’s success. These strategies have proved very beneficial and valuable for the organization’s overall benefit. It has resulted in more employees who participate more actively in training and development programs. The rise in employees has shown that success as a business has set up a wider variety of chains in its organization.
Recommendations
Organizational behavior is an essential concept that affects how an organization executes its tasks in a particular sector. Each organization wants excellent outcomes from its internal processes. To attain this aim, an organization must put in place efficient processes that encourage individuals in their workplaces to produce excellent outcomes.
References
Al-Hosani, A. A. (2011). Job satisfaction and knowledge sharing in oil and gas industry: the case of Adnoc company, Abu Dhabi. The British University in Dubai (BUiD),
Al Darwish, M. A. The Effect Of Artificial Intelligence In Smart Decision-Making In The UAE Government.
Alhammadi, Y. H. J. H., Tham, J., Azam, S. F. J. E. J. o. M., & Studies, M. (2020). LEADERS’BEHAVIOUR AND SITUATIONAL FACTORS ON THE ORGANIZATIONAL PERFORMANCE AT ABU DHABI NATIONAL OIL COMPANY (ADNOC).
Alhammadi, Y. H. J. H., Tham, J., & Azam, S. F. J. E. J. o. S. S. S. (2020). CONSTRUCTING LEADERS’BEHAVIOUR AND SITUATIONAL FACTORS TOWARD ORGANIZATIONAL PERFORMANCE AT ABU DHABI NATIONAL OIL COMPANY (ADNOC) IN THE UNITED ARAB EMIRATES (UAE).
Cheaitou, A., Larbi, R., & Al Housani, B. J. S.-E. P. S. (2019). decision making framework for tender evaluation and contractor selection in public organizations with risk considerations. 68, 100620.
El-Khatib, M., Al Qurashi, F., Al Brieki, S. J. A. J. o. I., & Management, B. (2021). Challenges of Design and Implementation of Program Governance—Cases from Government Bodies in UAE. 11(5), 566-581.
Marchau, V. A., Walker, W. E., Bloemen, P. J., & Popper, S. W. (2019). Decision making under deep uncertainty: From theory to practice. Springer.
