Policy title
The overcrowding of patients in the emergency department in the Dubai government sector
Description of Policy Problem
There is a problem related to emergency departments in Dubai healthcare. Despite numerous models of care that have been developed to reduce overcrowding and processing time in the emergency room, the current situation is not as favorable as it can be. Therefore, this problem has had a negative impact on both patients and medical staff. An extensive number of patients and the absence of the facilities necessary to provide qualified emergency procedures produce adverse outcomes (Kader, 2019). One possible reason is a lack of studies using quantitative and qualitative methods to investigate the extent of issues regarding the lack of resources that directly impact the level of healthcare. Such examinations could result in a reliable overview of the problem and an implementation of a remedy for the issue of inefficient management resulting in overcrowding.
What is the problem?
The current situation in the healthcare sector of Dubai revealed numerous problems associated with emergency departments. The issue is related to patient overcrowding in government emergency departments in Dubai city, which directly impacts the quality of service provided by healthcare workers.
Who is affected by the problem?
This problem has a considerable impact on both patients and medical staff.
Where does this problem take place?
The issue of overload and overcrowding takes place in emergency departments in government hospitals of Dubai and, therefore, results in an increase in infection rates. Researchers have examined these issues and found a maximization in violations during the last years, which correlates with the idea that Dubai requires additional safety measures and improvements (Al-Alawy et al., 2021a). Moreover, researchers mention that Dubai healthcare facilities will benefit from developing performance measures and specific regulations that address problems within organizational outcomes and patient satisfaction (Al-Alawy et al., 2021b). A study examining the same domain concluded that patients seeking healthcare services in Dubai are unsatisfied with the waiting time caused by significant influxes of people aiming to receive medical advice or treatment (Aburayya et al., 2020). The evidence proves that the city in question is the location that is most affected by overcrowded emergency rooms.
Since when is it happening?
Initially, the problem started in the early 1990s during the rapid development of the UAE. As the population has increased in a relatively short period of time, emergency departments were not fully equipped to assist such a large number of patients. This led to a shortage of beds in the emergency department.
Why is this a problem that the government should address?
The government should consider the following problem due to its contribution to social issues, lack of regulations, and market failures. UAE Vision 2020 specifically emphasizes the importance of having a world-class healthcare system, which directly correlates with improving patient satisfaction and risk mitigation (Salim & Rahman, 2017). Since the government illustrates the significance of addressing this domain, contributing to a more organized emergency department is one of the initial concerns that require improvement. In terms of social collapse, the issue elevates morbidity and mortality rates resulting in public health load. Moreover, the emerging obstacle of an increase in medical errors led to the burden associated with civil lawsuits and regulations issues (Strzelecka et al., 2021). In regards to market failure, the process detrimentally affects the resignation of emergency physicians resulting in a shortage of healthcare staff and emergency care facilities.
The rationale for government intervention
What are the key issues and sub-issues to be addressed?
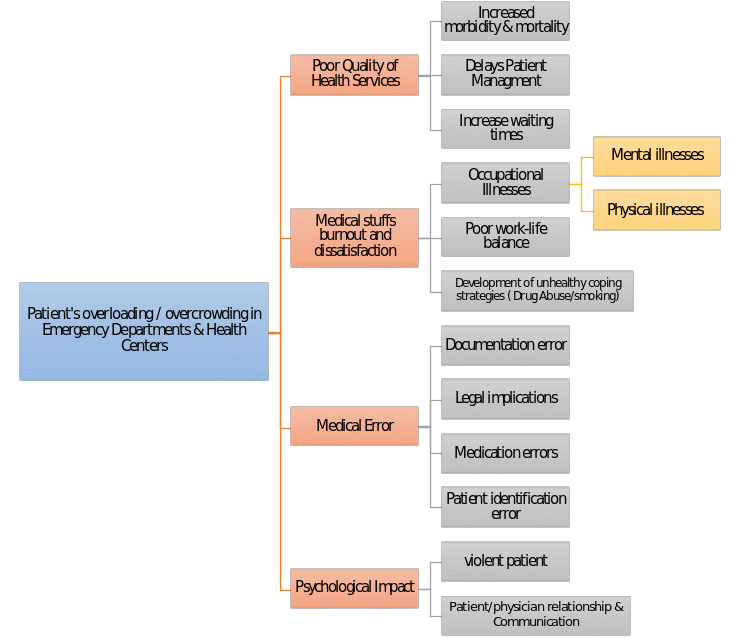
Patient overload and overcrowding in emergency departments cover various factors that affect the healthcare system. The first issue that could be addressed is the poor quality of healthcare service. An extensive number of patients and the absence of the facilities necessary to provide qualified emergency procedures produce negative outcomes (Kader, 2019). Firstly, it could lead to high morbidity and mortality levels associated with emergencies, including traumas and operations. Secondly, patient management procedures could be delayed due to the increased load on the medical staff. Lastly, the issue mentioned prior can potentially lead to an increase in waiting time, which is highly undesirable in emergency and acute situations.
Another problem associated with overcrowding and overload is professional burnout and dissatisfaction among healthcare workers. Medical staff is highly affected by stress and anxiety during a period of high workload. The consequences of the constant stress and anxiety could be dramatic for healthcare professionals leading to occupational illnesses, poor work-life balance, and the development of unhealthy coping strategies (Kader, 2019). The intense working schedule could lead to mental and physical illnesses among medical staff. Moreover, this problem could ruin the work-life balance affecting doctors’ and nurses’ both personal and professional lives. Attempting to cope with the stress and anxiety, therapists could develop harmful habits such as smoking, and drug, or substance abuse.
On the other hand, overcrowding and overload lead to common medical errors that could be avoided. High workload and stressful environment result in mistaken procedures. Common medical mistakes include documentation errors, legal implications, medication errors, and patient identification errors. Inappropriate implementation of the methods conducted without careful investigation could produce tragic outcomes (Kader, 2019). Errors in patient care, including documentation, medication, and diagnosis, bring a legal and administrative burden on the medical staff and the hospital.
Why is there a case for government intervention?
i.e., what happens if the government does not intervene? Please refer to the slide in the class regarding justifications for government intervention.
Governmental support and intervention are required because of the effect on the healthcare system in the UAE. If this tendency remains unchanged, it will harm the image of healthcare workers (Muslim, 2019). Moreover, the problem mentioned above, such as poor quality of healthcare services, professional burnout, dissatisfaction, and an increased number of medical errors, will ruin the country’s healthcare system (Muslim, 2019). Government should take action as the quality of health-related services will affect the quality of life of the general population (Muslim, 2019). Moreover, this issue could create a private emergency healthcare sector leading to financial loss in medicine.
Policy Objectives
What are the policy objectives?
Please be as precise as possible (quantify). Specify both outputs and outcomes. You will refine these objectives after doing more analysis on the topic.
The outcomes that will follow after the policy is implemented are:
- To provide all required equipment and materials necessary to eliminate the problem.
- To reduce the overburden on medical staff and increase the quality of the service.
The outputs that will result in the follow-up strategic actions are:
- Encourage the population’s trust in the healthcare system
- To increase the awareness of the public about overcrowding and overload issues.
- Suggest adequate strategies after analyzing the current situation.
Policy Context
Is it a new policy?
The offered policy is a unique approach to the existing problem. According to the UAE Healthcare Department (n.d.), a similar strategy has never been implemented prior. A similar model based on identical desired outcomes was proposed in Iran in 2015, aiming at effective overcrowding management (Babatabar-Darzi et al., 2020). Successful experience of the neighboring countries and Western models could help cope with the issue in question by acting as real-life examples and helpful information that can give an overview of the potential future.
Policy Scope
What are (at a high level) the main preliminary policy instruments/interventions to be considered?
The measures that will be considered to address overcrowding are:
- Community Awareness
- Creating a list of critical diseases directed towards paramedics in case patients in the red zone contact physicians.
- Giving doctors in the emergency department triaging training.
- Encouraging the community to visit PHC by making access easy.
- Increasing the number of PHC clinics in the community.
- Connecting emergency doctors and PHC with the paramedics to develop policies.
- Planning strategies to manage physicians’ professional burnout.
- Ensuring instantaneous and appropriate responses to emergency cases.
- Providing protected emergency care services.
Will the policy apply only in Dubai?
The policy will be implemented in Dubai city and be available for all patients delivered to government emergency departments.
High-Level Information Requirement
What information, data, cost information, etc., will you need to find to carry out the analysis of the policy?
This is a new policy directed at improving the quality and satisfaction of patients and medical staff. As this strategy was not implemented before in the given region, it requires careful investigation and research. The central strategic development will rely on the experience of a foreign country and will be adapted to the local lifestyle. The existing platform that has adequate measures in regard to quality patient care is the Joint Commission of International Accreditation (JCIA). Another system that will be utilized is the Canadian Triage. The method illustrates the acuity of the patient’s state.
Key Stakeholders
The key stakeholders in the government
The following parties involved in policy implementation have been identified:
- Medical Staff.
- Emergency department.
- Primary health care centers.
- Community patient.
- DHA.
The key stakeholders that will be directly or indirectly affected by the policy
Affected stakeholders:
- Governmental institutions.
- Healthcare Department of the government hospitals in Dubai.
- Joint Commission International Accreditation (JCIA).
- World Federation of Public Health Associations (WFPHA).
References
Aburayya, A., Alshurideh, M., Albqaeen, A., Alawadhi, D., & A’yadeh, I. A. (2020). An investigation of factors affecting patients waiting time in Primary Health Care Centers: An assessment study in Dubai. Management Science Letters, 1265–1276.
Al-Alawy, K., Moonesar, I. A., Mubarak Obaid, H. A., Al-Abed Bawadi, E. I., & Gaafar, R. (2021a). Hospital accreditation: A review of evidence, regulatory compliance, and healthcare outcome measures. Dubai Medical Journal, 4(3), 248–255. Web.
Al-Alawy, K., Azaad Moonesar, I., Ali Mubarak Obaid, H., Gaafar, R., & Ismail Al-Abed Bawadi, E. (2021b). A mixed-methods study to explore the impact of hospital accreditation. INQUIRY: The Journal of Health Care Organization, Provision, and Financing, 58, 004695802098146.
Babatabar-Darzi, H., Jafari-Iraqi, I., Mahmoudi, H., &Ebadi, A. (2020). Overcrowding management and PATIENT safety: An application of the Stabilization model. Iranian journal of nursing and midwifery research.
Kader, B. A. (2019). New steps to reduce crowding at Emergency units in Abu Dhabi. Health – Gulf News.
Muslim, N. (2019). Public hospitals to charge only after patient stabilises. Health – Gulf News.
Salim, F. M., & Rahman, M. H. (2017). The impact of Joint Commission International Healthcare Accreditation on Infection Control Performance: A Study in Dubai hospital. GATR Global Journal of Business Social Sciences Review, 5(1), 37–45.
Strzelecka, A., Stachura, M., Wójcik, T., Kordyzon, M., Chmielewski, J. P., Florek-Łuszczki, M., & Nowak-Starz, G. (2021). Determinants of primary healthcare patients’ dissatisfaction with the quality of provided medical services. Annals of Agricultural and Environmental Medicine.
UAE Healthcare Department. (n.d.). Health strategies, policies and laws – the official portal of the uae government.
